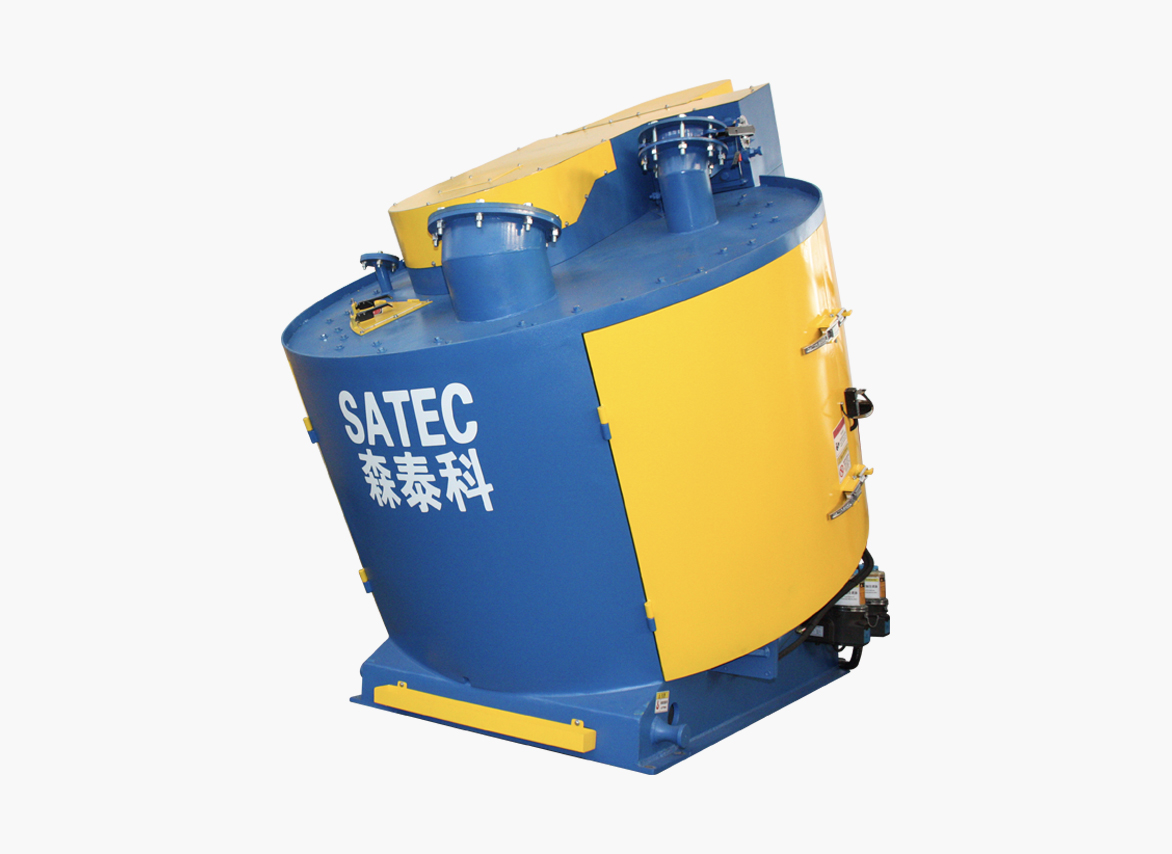
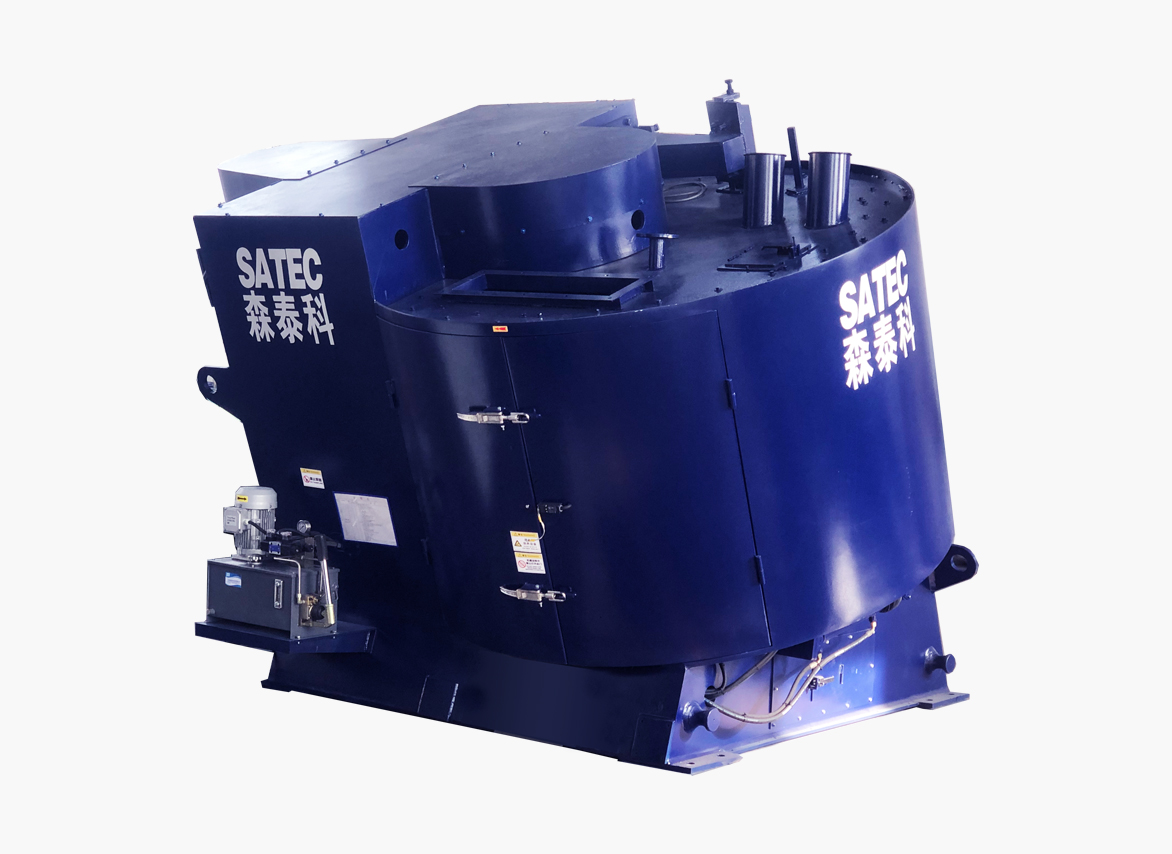
Metallurgical Industry Mixer: Pelletizing Metallurgical Mixer
This is a processing method that transforms finely ground concentrate into materials that meet smelting requirements. The process involves mixing prepared materials in a specific ratio, rolling them in a pelletizer to form green pellets of a certain size, and then using drying, calcination, or other methods to cause a series of physical changes that harden and solidify them. This process is called pelletizing, and the product is called pellet ore. A mixture of concentrate powder and flux is rolled into green pellets in a pelletizer, then dried, calcined, and solidified to become an iron-containing raw material with good metallurgical properties, supplying the needs of iron and steel smelting. The main processes in pelletizing production include raw material preparation, batching and mixing, pelletizing, drying and calcination, cooling, finished product processing, and return ore treatment. The raw materials for pellet ore production are mainly concentrate powder and additives; if solid fuels are used for calcination, pulverized coal and coke powder are also used. The purpose of mixing and granulation of sintering materials is as follows: Mixing ensures uniform distribution of components, reducing segregation; it ensures uniform wetting of the material, stabilizing the material's moisture content; it preheats the material, increasing its temperature; and it produces granules of suitable size, improving the permeability of the sintering layer.
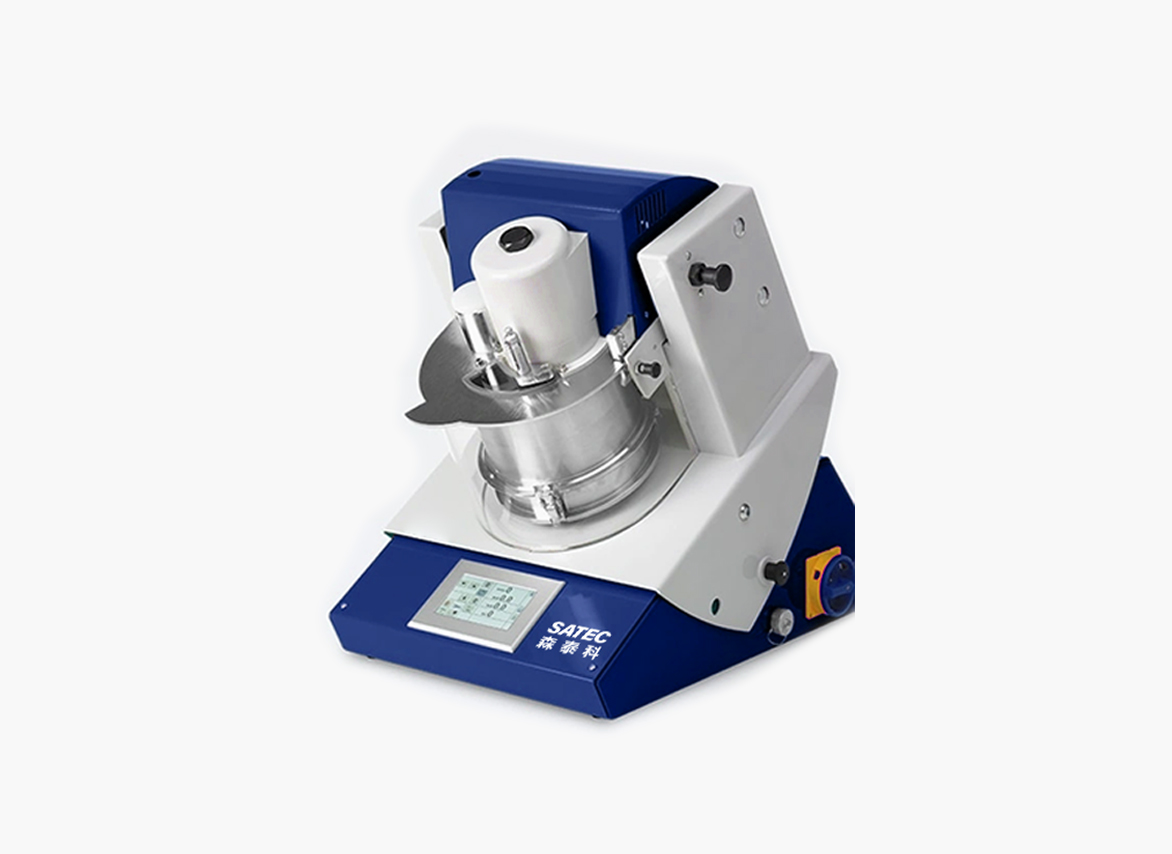
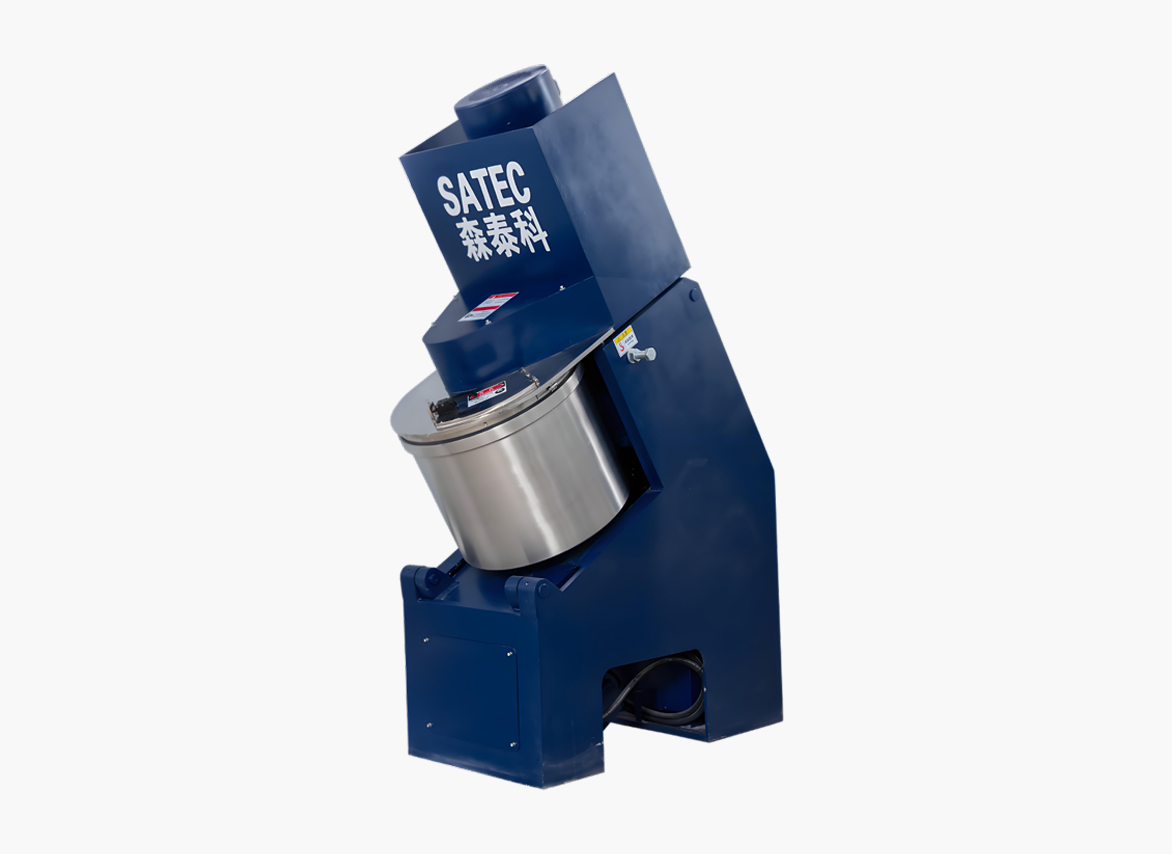
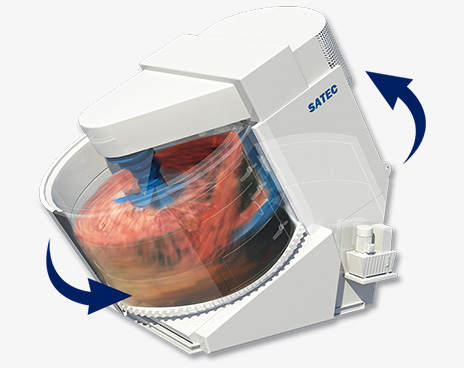
Mixing time is related to the mixer's length, rotational speed, and tilt angle. Increasing the mixer length undoubtedly extends the mixing and granulation time, which is beneficial for mixing and granulation. The mixer's rotational speed determines the material's movement within the pan. If the speed is too low, the centrifugal force generated by the pan is weak, making it difficult for the material to reach a certain height and form an aggregated state, resulting in low mixing and granulation efficiency. However, if the speed is too high, the centrifugal force generated by the pan is too great, causing the material to adhere tightly to the pan wall, thus completely losing its mixing and granulation function. The mixer's tilt angle determines the material's residence time within the machine. The larger the tilt angle, the shorter the mixing time, and the worse the mixing and granulation effect. When using a cylindrical mixer for primary mixing, its tilt angle should be less than 2.0°; when used for secondary mixing, its tilt angle should be no less than 1.5°.
Qingdao SATEC Electro-Mechanical Technology Co., Ltd.'s mixing and granulating machine is designed to meet the requirements of pellet production. The equipment is an inclined machine with an angle optimal for uniform material mixing, facilitating easy feeding and discharging and preventing excessive material accumulation in the pan. Its unique design allows for individual speed adjustment of components, adjusting the rotation speed according to the material's rotational requirements to achieve optimal mixing and avoid problems such as material buildup, poor mixing and granulation, and insufficient mixing and granulation due to excessive rotation speed. Its scientifically designed structure minimizes the need for maintenance and wear of parts, and the internal scraper ensures thorough material discharge.
Furthermore, the filling rate of the mixer also affects the mixing and granulation effect of the mixture. The filling rate is expressed as the volume occupied by the mixture in the pan. If the filling rate is too low, the output is low, and the interaction forces between materials are weak, which is detrimental to mixing and granulation. If the filling rate is too high, while increasing the output with a constant mixing time, the increased material layer restricts and disrupts material movement, which is also detrimental to mixing and granulation. A suitable filling rate for the first mixing stage should be around 15%, while the filling rate for the second mixing stage should be lower than that for the first. When the material lining inside the mixer is insufficient, the amount of water added should be increased to increase the surface water of the mixture (water is added directly to the material surface). If too much material adheres to the mixer, the amount of water added should be reduced.
Excessive material buildup on the inner wall of the pan should be avoided. Cleaning should be performed by evacuation during shutdown to maintain good mixing and pelletizing capacity.
The control of water supply during material changes and slowing down must be appropriate to avoid the occurrence of "dry" or "wet" material being fed into the system.
Suitable for the preparation of metallurgical sintering mixtures and pellets, and the recovery and utilization of iron-containing dust, sludge, and slag dust in steel plants and non-ferrous smelters.
◎ Improves the permeability of sintering materials
◎ Increases pelletizing rate and produces high-strength green pellets
◎ Reduces the amount of bentonite used
◎ Reduces the amount of coke powder used
◎ Increases output and saves fuel, improving profit margins





 Environmental friendly
Environmental friendly Lithium battery
Lithium battery Chemical Industry
Chemical Industry Catalyst
Catalyst Ceramic
Ceramic Medical Food
Medical Food Metallurgy
Metallurgy Carbon
Carbon Fertilizer
Fertilizer Building materials
Building materials Foundry Sand
Foundry Sand Welding Flux
Welding Flux Glass
Glass Refractory
Refractory



